Aluminum is all around us — it’s used in household appliances, parts for different types of vehicles and in drink cans and packaging foil. It’s a widely used material as it is lighter than iron, almost as durable as steel, corrosion-resistant and pliable. Aluminum is also a good heat and electrical conductor and is often used in the sand casting process due to its high strength-to-weight ratio.
The U.S. is one of the largest importers of unwrought aluminum and aluminum alloys. Explore where this material comes from, how it’s sourced and where the U.S. gets it from to keep up with demand.
How Is Aluminum Sourced?
Even though aluminum is one of the most abundant metal elements in the Earth’s crust, it is not a natural metal. Bauxite ore is the main source of aluminum, which must be extracted by combining it with oxygen or different elements. Bauxite rocks form from red clay material and are commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Contrary to other minerals that can be separated by melting, sourcing aluminum is a complicated process that requires a significant amount of energy. The process of how aluminum is extracted typically involves several steps:
- Bauxite mining: Bauxite ore is mined and transported to processing plants.
- Alumina production: The Bayer process is used to extract alumina. It involves crushing the ore, dissolving it in a sodium hydroxide solution, separating impurities and precipitating alumina as a white powder.
- Aluminum extraction: The alumina is sent to smelters where it is heated and transformed into molten aluminum.
- Aluminum casting: The molten aluminum is cast into different shapes, such as ingots or sheets, which can be further processed into various products.
Extracting aluminum requires careful consideration of many factors, such as environmental impact, labor conditions and supply chain transparency. Responsible sourcing practices aim to minimize negative effects on the environment and ensure fair working conditions for the people involved in the process. For example, during the land clearing process prior to mining, the topsoil is stored so it can be replaced during rehabilitation. With these environmental conservation efforts, an average of 80% of the ecosystem is returned to its native state.
Where Does Aluminum Come From?
Bauxite was named after the French village of Les Baux where geologist Pierre Berthe found the ore in nearby deposits and discovered that it contained aluminum. Today, aluminum is sourced from various places around the world. The global nature of the aluminum industry ensures a diverse supply chain, with some countries specializing in different stages of the production process. Some countries are known for producing bauxite while others have significant alumina refining and aluminum production capacity.
Many countries have a strong presence in the aluminum industry in terms of both production and consumption, and they often rely on a combination of domestic production and imports. This interdependence ensures a steady supply of aluminum to meet the growing demand from various industries worldwide.
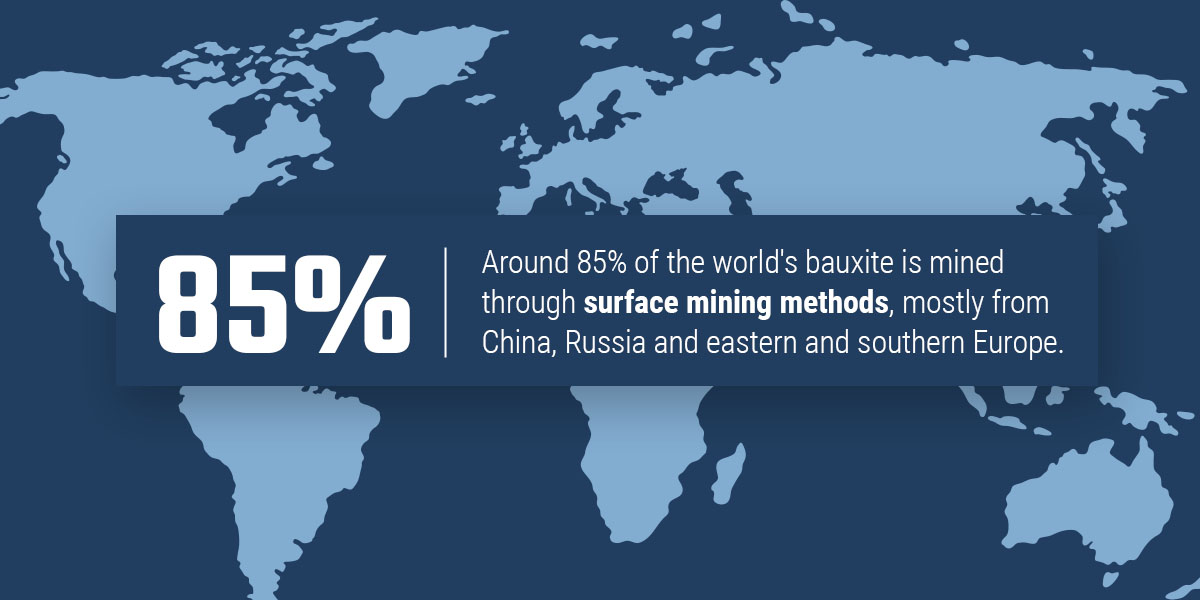
Around 85% of the world’s bauxite is mined through surface mining methods, mostly from China, Russia and eastern and southern Europe. Here are the top 10 aluminum-producing countries in the world:
- China leads by producing more than half of the world’s aluminum output.
- India is home to the world’s leading aluminum-rolling company.
- Russia is the location of RUSAL’s headquarters, the leading global aluminum producer.
- Canada has 10 primary aluminum smelters and an alumina refinery, with the majority operating in Quebec.
- The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is the largest aluminum producer in the Middle East.
- Bahrain operates the biggest single-site aluminum smelter in the world.
- Australia produces around 1.5 million metric tons of aluminum per year, despite heavy energy costs associated with smelter operations.
- Norway is the largest exporter of primary aluminum to the European Union (EU) along with Iceland.
- The U.S. has three companies that operate six primary aluminum smelters in five states.
- Iceland is seeing a rise in new green aluminum production technology to lower the carbon footprint of these operations.
Where Does the U.S. Get Its Aluminum From?
Even though the U.S. is one of the top aluminum producers globally, the majority of unwrought aluminum and aluminum alloys are imported. Imports happen through various channels, including trade agreements, direct sales involving contracts, industry trends and sustainability and international market dynamics.
The following countries account for more than 80% of all U.S. aluminum imports:
- Canada
- China
- Mexico
- UAE
- Bahrain
- India
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Germany
- Australia
- Russia
- Turkey
- Argentina
- Vietnam
- Colombia
A majority of the imports come from European markets because their extraction and sourcing process is great for alloys. In fact, about one-third of the EU’s aluminum exports go to America. Europe has an established and complete aluminum value chain, from extracting bauxite and primary metal production to semi-fabrication and recycling.
Additionally, the European aluminum industry is trying to incorporate a holistic approach to sustainability, which is beneficial for American-based companies looking for clean aluminum.
Why Do We Import Aluminum?
Importing aluminum offers several advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: Importing aluminum from other countries with lower production costs can be more cost-effective compared to producing it domestically. This allows businesses to access aluminum at competitive prices, reducing manufacturing costs and making products more affordable for consumers.
- Diverse product range: Importing aluminum ensures access to a wider range of specialized aluminum products that may not be readily available domestically. As a result, companies can meet specific requirements or cater to niche markets that require unique aluminum products or alloys.
- Market efficiency: Imports ensure there’s a steady supply to meet demand, especially during periods when domestic production is limited. The U.S. can prevent shortages by tapping into global markets with different production capacities and seasonal variations.
- Technological advancements: Importing makes it easier to take advantage of advanced or green manufacturing technologies and processes, helping us benefit from quality improvements and clean aluminum.
- Global trade relationships: Sourcing aluminum from outside the country fosters trade relationships and partnerships with other countries, promoting economic cooperation, stimulating job growth and encouraging investing endeavors.
Contact Warner Brothers Foundry Company for High-Quality Aluminum Alloys
While many foundries only work with a handful of common alloys, we handle a wide range of aluminum-based alloys. We understand that every project is unique, no matter the industry. Our team is dedicated to helping you and your company with your aluminum casting needs, whether you’re looking for prototypes or production material. Only the highest-quality, certified ingot is used to produce aluminum casting.
Browse our aluminum alloy specs sheets or get in touch with us to request a quote.